The Different Types of Broadband Networks Explained

In our digital era, reliable internet isn't just nice to have—it's a necessity. Broadband is the backbone of this connectivity, but what type suits you best? From lightning-fast fiber optic to widely available DSL, this guide dives into the various broadband networks. Designed for tech enthusiasts, families, and businesses alike, we're here to simplify your choice with clear, expert advice. Let's demystify the options and find your perfect online companion.
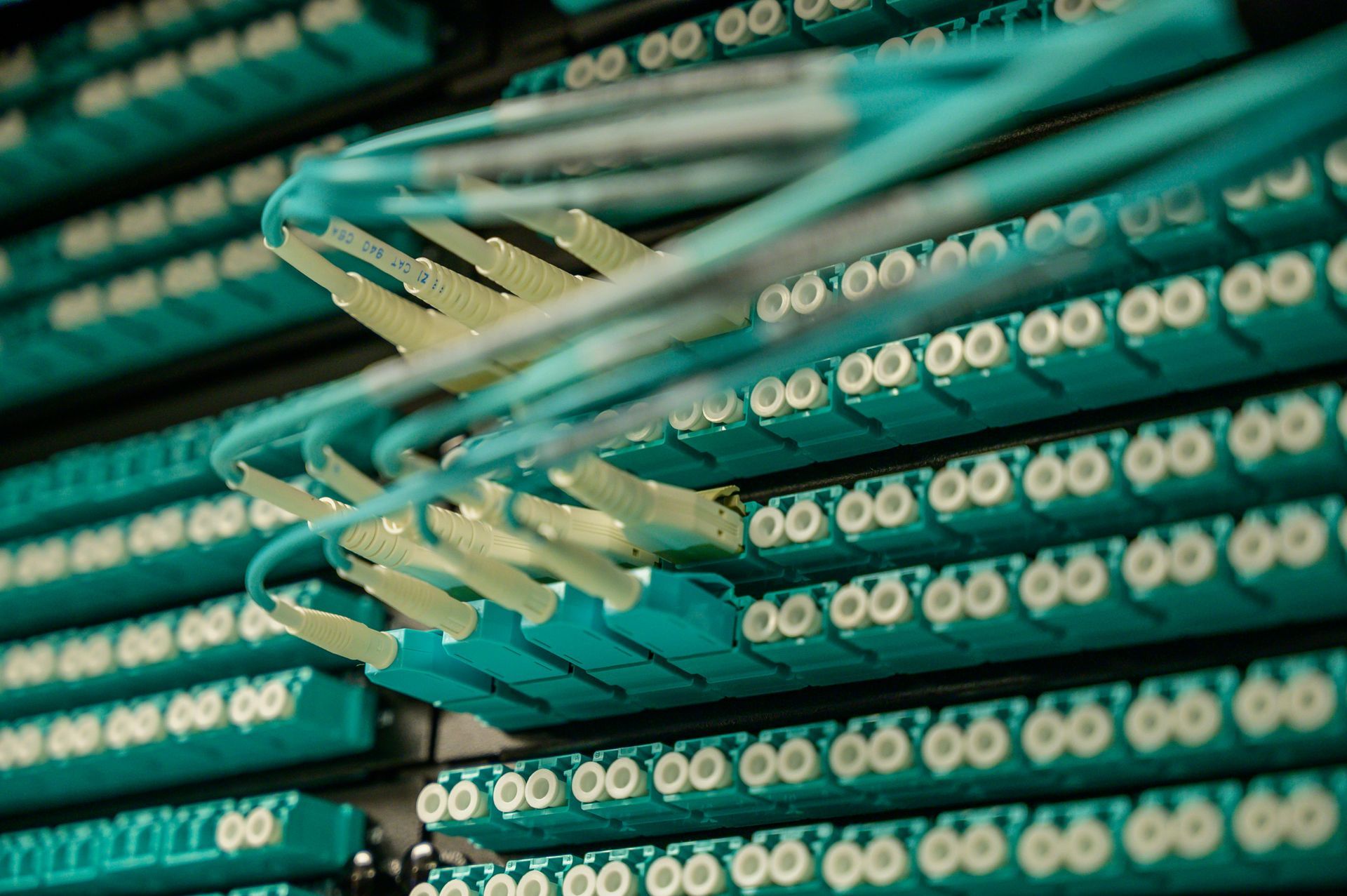
Fiber Optic Broadband
Fiber optic broadband uses thin glass fibers to deliver the internet at extremely high speeds. It's the fastest option available, perfect for anyone needing quick uploads and downloads, like heavy streamers, online gamers, and businesses.
Pros
- Speeds: Offers the fastest internet speeds for both uploading and downloading data.
- Consistency: Provides stable connections, not easily affected by weather or distance.
- Future-Ready: Can handle increasing data needs without needing major upgrades.
Cons
- Limited Reach: Not every area has fiber; it's mostly in cities or new developments.
- Higher Cost: Generally pricier than other broadband options due to its advanced technology.
Fiber is best for those who prioritize speed and reliability and are in areas with fiber infrastructure. Despite its higher price, its performance is unmatched.
Cable Broadband
Cable broadband uses the same coaxial cables that deliver your cable TV, making it widely available in many areas, especially where cable TV is common. It's a step down from fiber in terms of speed but still offers more than enough for most households and small businesses.
Pros
- Speed: While not as fast as fiber, cable internet is speedy, supporting streaming, gaming, and downloading with ease.
- Availability: More widespread than fiber, since it uses existing cable TV infrastructure.
Cons
- Speed Fluctuations: Your internet speed can slow down during peak usage times because you share bandwidth with neighbors.
- Not as Fast as Fiber: While fast, it can't match the top speeds that fiber optic offers.
Cable broadband is a solid choice for those who need reliable and fast internet but don't have access to fiber or find fiber's cost prohibitive. It strikes a balance between speed and availability, making it a popular option for many.
DSL (Digital Subscriber Line) Broadband
DSL broadband brings the internet to you through the existing telephone lines. It's one of the most widely available types of broadband, reaching areas where other types, like fiber, might not be accessible.
Pros
- Accessibility: DSL is available in most areas, including rural ones, because it uses the telephone network.
- Affordability: Generally cheaper than both fiber and cable options, making it a budget-friendly choice.
Cons
- Distance Matters: The further you are from the provider's facility, the slower your internet speed will be.
- Slower Speeds: DSL can't compete with the speeds offered by fiber or high-end cable connections. It's suitable for basic browsing and streaming but might struggle with high-demand activities like HD streaming or competitive gaming.
DSL is an excellent option for those in remote locations or looking for a more affordable internet solution. While it doesn't offer blazing speeds, it provides a reliable connection for everyday use.
Choosing the Right Broadband for You
Selecting the best broadband for your needs depends on a few key factors: your location, internet usage, and budget. Here's how to make an informed choice:
- Location: Fiber's superior speed and reliability are enticing, but it's not available everywhere. Cable offers a good balance of speed and availability, while DSL covers the most ground, especially in rural areas.
- Internet Usage: For heavy-duty tasks like 4K streaming, competitive online gaming, and large file downloads, fiber is your best bet. Cable is suitable for moderate to heavy use, including streaming and gaming. DSL is adequate for basic browsing, emails, and standard-definition streaming.
- Budget: Fiber tends to be the priciest option, reflecting its high speed and reliability. Cable comes in middle, offering a good compromise between cost and performance. DSL is the most wallet-friendly, especially for users with lighter internet needs.
Before making a decision, check what's available in your area and compare plans from different providers. Consider not just the monthly cost but also installation fees, equipment rentals, and any data caps or speed limitations. Sometimes, providers offer bundles with TV or phone services, which might save you money if you're interested in those services as well.
Conclusion
In our journey through the world of broadband, we've unpacked the differences between fiber optic, cable, and DSL internet. Each offers unique advantages and comes with its own set of limitations. The right choice varies based on your personal or business needs, your location, and how much you're willing to spend.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I get broadband without a phone line?
Yes, you can get broadband without a traditional phone line. Fiber optic and cable broadband connections do not require a phone line. Some DSL providers also offer "dry loop" DSL, which is DSL without a phone service.
Why do broadband speeds vary by location?
Broadband speeds can vary due to the type of connection, the distance from the service provider's central office (in the case of DSL), network congestion, and the quality of the infrastructure in your area.
How do data caps affect broadband usage?
Data caps limit the amount of data you can download or upload in a month. Exceeding these caps can result in additional charges or slowed down internet speeds. It's important to choose a plan that fits your data needs.
What's the difference between download and upload speeds?
Download speed is how fast you can receive data from the internet, crucial for streaming videos or browsing the web. Upload speed is how fast you can send data to the internet, important for video calls, online gaming, and uploading large files.
How can I improve my broadband speed?
Improving broadband speed can involve upgrading your plan, using a wired connection instead of Wi-Fi, optimizing your router's placement, and minimizing the number of devices connected simultaneously.
What are the emerging alternatives to traditional broadband?
Emerging alternatives include 5G wireless broadband, offering high speeds and low latency over cellular networks, and satellite internet, which is improving in speed and reliability, providing more options for rural and remote areas.
Can I switch broadband providers if I'm not satisfied?
Yes, you can switch broadband providers if you're not satisfied with your current service. Check your contract for any early termination fees and compare other providers' offers, speeds, and prices in your area.